Sepsis is a very serious condition caused by the body’s uncontrolled immune response to an infection and can lead to organ failure or death. The body normally releases certain chemicals and proteins in response to an infection. Their job is to regulate the body’s immune response, inflammation and wound healing. In sepsis, these chemicals and proteins produce an exaggerated response leading to a widespread reaction throughout the body.
The health risks of sepsis are numerous. Sometimes called blood poisoning, sepsis impedes blood flow to vital organs and causes abnormal blood clotting. When identified in the early stages, sepsis is usually treatable but, if the response is not stopped, it can lead to multiple organ failure, septic shock (the most severe stage of sepsis) and even death.
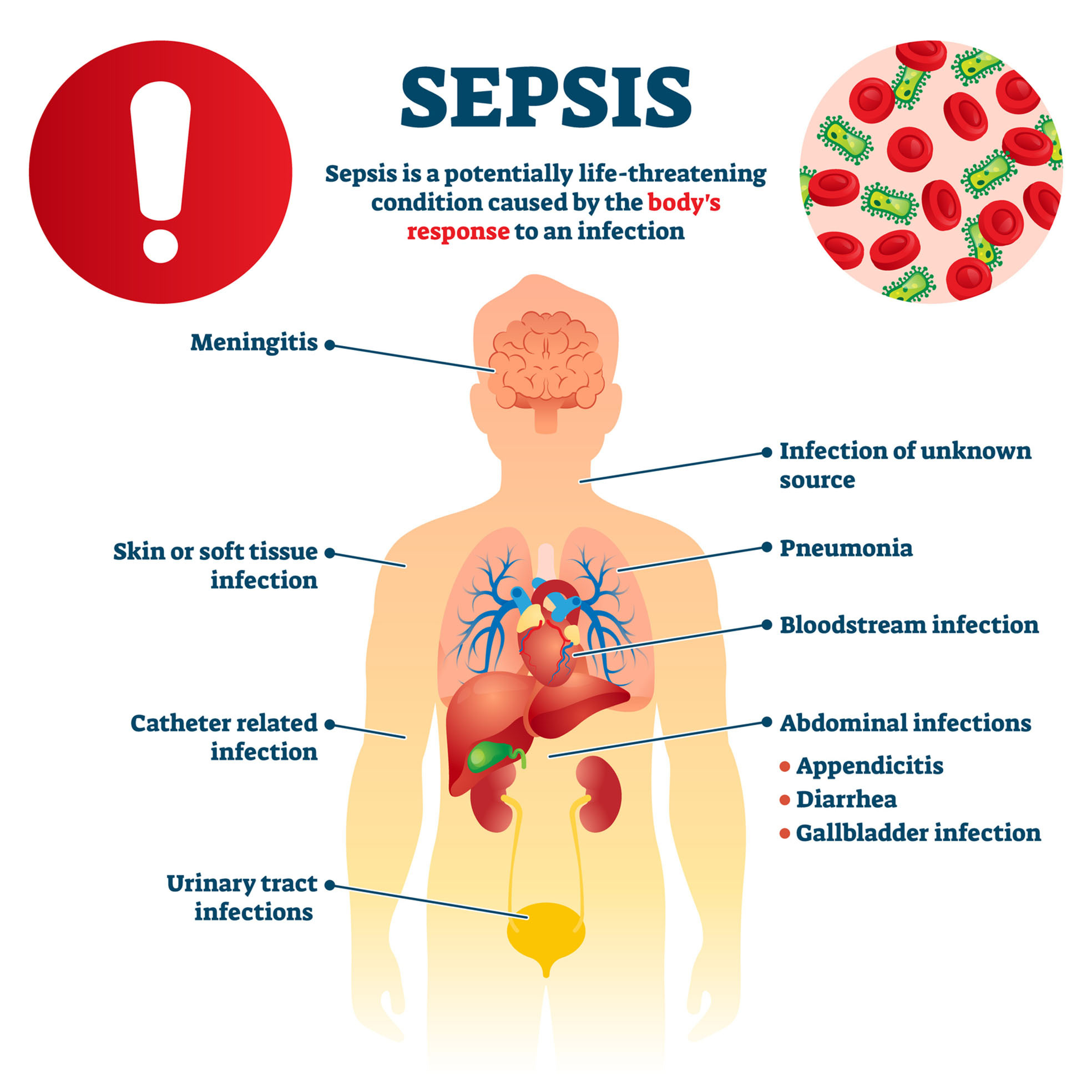
Causes of Sepsis
The most common cause of sepsis is a bacterial infection, but the condition is also linked to the following:
- Fungal infections
- Viral infections
- Parasitic infections
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the area of the body where the infection started. Early recognition is important so treatment can be initiated as soon as possible. Common signs and symptoms of sepsis include:
- Fever (or low body temperature)
- Chills or shivering
- Confusion or altered mental capacity
- Rapid or difficult breathing
- Fast heart rate
- Low blood pressure
- Rapid pulse
- Clammy skin
- Extreme pain or discomfort
- Cold extremities
- Cyanotic (bluish/gray) skin or mottling
- Low urine output
Those at Risk
Sepsis can occur at any age in those with infection but there are certain groups at higher risk, including:
- Adults over the age of 65
- Infants under the age of one
- Pregnant women
- Individuals with compromised immune systems
- Hospitalized patients
- Those with chronic medical conditions such as cancer, diabetes, lung conditions and kidney disease
- Individuals with serious injuries such as burns or large wounds
- Patients with IVs or catheters
How Is It Diagnosed?
Identifying the source of infection requires careful, and full, investigation. Tests may also be performed to evaluate organ function. Diagnostic testing often includes:
- Blood tests to look for signs of infection such as abnormal white blood cell counts or bacteria, clotting issues or other signs of sepsis
- Blood cultures, if infection is found
- Urine tests to identify infection in the urinary tract
- Wound or respiratory samples
- Chest X-ray to identify lung infections
- CT scans which can reveal organ infections
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) to look for bone or soft tissue infection
If an organ or organs appear at risk, a scoring system may be used to determine if function is declining.
Treatment Options
Sepsis is a gravely serious condition and patients are usually placed in an intensive care unit for treatment. The goal of treatment is to stop the infection, prevent organ failure and regulate blood pressure. Patients are closely monitored for deteriorating organ function and to track progress or decline. The following treatments may be administered:
- Antibiotics
- IV fluids
- Respiratory support including medication, oxygen or placement on a ventilator
- Kidney dialysis
- Surgery to remove infection or tissue damaged by infection
Prevention Tips
Since 80 percent of sepsis cases occur outside the hospital, taking steps to reduce the risk of sepsis at home is important. The below tips are recommended:
- Good handwashing and hygiene
- Keep wounds and cuts clean and cover until healed
- Use safe food preparation techniques
- Monitor and treat chronic conditions
- See your doctor or healthcare provider immediately if you have an infection that is not improving or is worsening
The content of this site is for informational purposes only and should not be taken as professional medical advice. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding any medical conditions or treatments.