Since COVID-19 was declared a pandemic, most of us continue to hear about our immune system. Our immune system is a vast network of cells and tissues. The purpose of these cells and tissues is to act as a natural defense mechanism for our body and fight off invading germs and pathogens. A healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet supports our immune system function, which helps keep us free from infection.
A healthy lifestyle generally includes balanced eating, exercise, stress management and quality sleep. Aim for 30 minutes of exercise at least five days per week. Exercise doesn’t have to be strenuous, just get moving in any way that you like. Walking, yoga, dancing and strength training all provide health benefits. Some benefits provided by exercise overlap with things needed to support our immune system, like stress management and better sleep.
Couple these things with a balanced diet to best support your immune system. A balanced diet should include fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats, added sugars and alcohol. This eating pattern provides protein, vitamin C, vitamin D and zinc, which are key to supporting immune health. These nutrients are widely found in a variety of foods. Below are some examples of how smart nutrition choices can support your immune system.
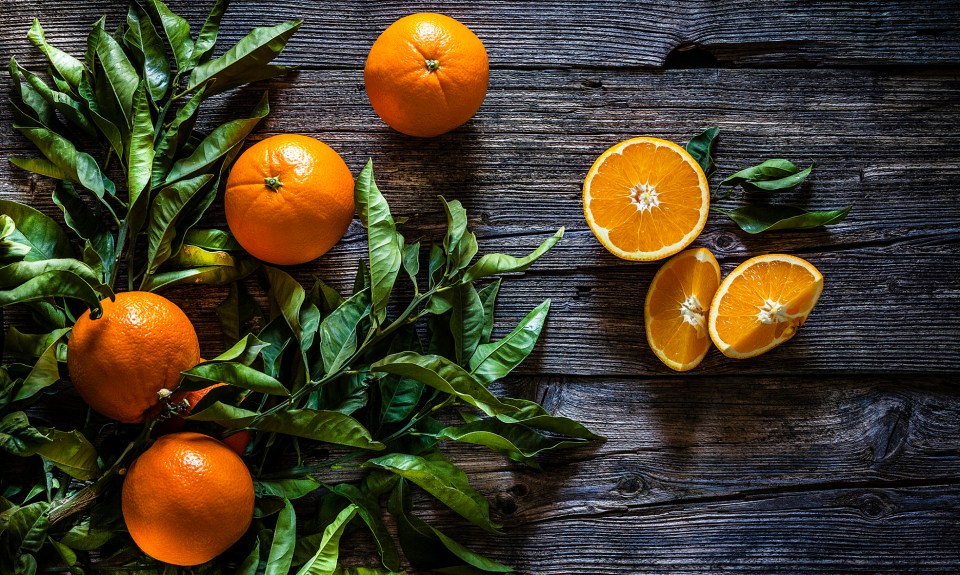
Vitamin C
Vitamin C has antioxidant effects in our body, supports skin and tissue cells and is needed for leukocyte function to fight infection. The daily recommended intake for vitamin C is 75mg for women and 90mg for men. Vitamin C can be found in foods such as:
- Citrus fruits
- Kiwi
- Strawberries
- Broccoli
- Bell peppers (Just a half cup of yellow bell peppers has 137mg of vitamin C!)
Zinc
Zinc is needed for development, growth and proper function of immune cells. In addition to immune health, zinc also helps maintain our sense of taste and smell. It can be found naturally in some foods and is often added to over-the-counter cold remedies. Recommended daily intake for zinc is 8mg for women and 11mg for men. You can find zinc in these foods:
- Oysters
- Meat, such as beef and poultry
- Chickpeas
- Seeds (for example, pumpkin or hemp seeds)
- Whole grains
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that supports our immune system, has hormone functions and plays a role in bone health. Maintaining adequate intakes of vitamin D can be protective against infection. During the warmer months, sunlight exposure can provide us with vitamin D. However, during the colder winter months when we have less sunlight exposure, obtaining sources of vitamin D in the diet is important. These sources include:
- Fatty fish, such as salmon
- Egg yolks
- Fortified dairy products, such as milk and yogurt
- Fortified cereals
Protein
Protein is essential to help produce immune system cells and antibodies. Requirements vary depending on health conditions. A general guideline is 0.8 to 1 gram of protein for every kilogram of bodyweight. Protein can be obtained from a variety of sources, including animal and plant products. If obtaining protein from animal products, aim for heart healthy sources such as lean ground turkey or chicken, chicken breasts and fish. Plant proteins can be found in chickpeas, quinoa or plant-based protein powders.
To follow a healthy eating pattern at meal time, fill one quarter of a 9-inch plate with protein, one quarter with whole grains, half with non-starchy vegetables and include a side of fruit. A balanced dinner could look something like this: salmon, quinoa, half a plate of roasted broccoli and a cup of strawberries on the side. These smart nutrition choices will provide you with each of the key immune-supporting nutrients mentioned above!
Samantha White is a dietitian at Novant Health Rehabilitation Hospital, an affiliate of Encompass Health
The content of this site is for informational purposes only and should not be taken as professional medical advice. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding any medical conditions or treatments.